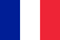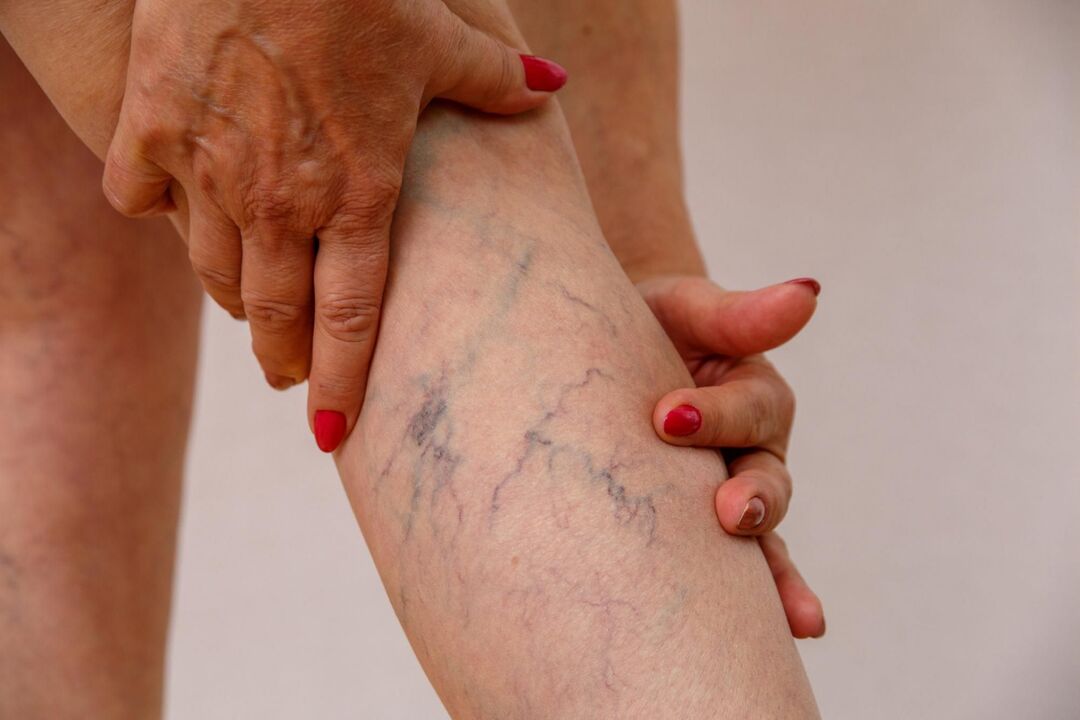
Varicose veins are a vascular pathology when, against the background of the weakness of the connective tissue, the stretching of the venous wall of the vein occurs. The diameter of the vein increases, and its wall becomes thinner.
The large diameter of the vein leads to a decrease in the speed of blood flow, venous congestion and contributes to pain in the calves. Against this background, varicose veins can lead to thrombophlebitis - inflammation of the affected veins, which is terrible for the development of thromboembolic complications. Visible external cones along the vessels allow you to recognize varicose veins in the legs. Varicose veins of the lower extremities (ICD code I83) is a very visible disease that is easily dismissed.
Varicose veins in the esophagus are included in the symptoms of portal hypertension, and secondary varicose veins in the female perineum indicate varicose veins of the small pelvis and difficulty in blood flow from the main veins.
Varicose veins of the spermatic cord (varicoceles) are manifested by the clinic of secondary pelvic phlebohypertension and can lead to infertility in men. The etiology and pathogenesis of varicose veins are very different depending on the localization of the process. In itself, the increase in the diameter of the veins is not dangerous, but the complications of varicose veins carry a great risk to the health, and sometimes even to the patient's life. The cause of the appearance of varicose veins in the legs can be heavy physical exertion, childbirth, a sedentary lifestyle of patients.
To understand what varicose veins look like, it is enough to go to the summer beach. Although many carriers of varicose veins are ashamed to show themselves there, you will definitely see how varicose veins manifest themselves in men and women. The disease is so widespread that you will definitely see it. After reading this article to the end, you will understand how easy it is to treat varicose veins. Do not be afraid to go to the phlebologist.
Can we reverse varicose veins?
Many people ask this question, hoping to cure varicose veins in the initial stage with the help of medicines or traditional medical methods. If we are talking about varicose veins in the legs, then phlebologists can answer this question unequivocally - the degenerative destruction of the venous wall cannot disappear without turning off the affected vein from blood circulation or removing it.
It happens that dilated veins may still not lose their function and increase in volume due to the overflow of blood from the upper sections, and the pump of the muscles of the lower part of the leg helps to flow blood into the deep veins.
Depending on the stage of varicose veins, different surgical and conservative treatment methods can be applied that can stop the progression of varicose veins at different stages. The order here is this: if the vein is irreversibly affected, then it must be removed or clotted or sutured.
Why are initial varicose veins irreversible without surgical intervention? For the effective treatment of varicose veins in the legs, it is necessary to distinguish where the pathological discharge of venous blood comes from and remove it with minimal trauma. However, enlarged branches with varicose veins can restore their function on their own and without surgical intervention if the phlebologist eliminates pathological discharges, which cause varicose veins and irreversibly changed veins.
Modern varicose vein treatment has advanced significantly since the first varicose vein surgeries on men and women in the 19th century. Depending on the degree of varicose veins, a classification of the disease and appropriate treatment methods are compiled.
The clinics of the Innovative Vascular Center know how to treat varicose veins with minimal medical, psychological and cosmetic concerns. We do not need to remove varicose veins according to the classic scheme. In the arsenal of phlebologists, the hemodynamic concept of treating the main causes of varicose veins, a technique that includes the correction of only the pathologically altered venous outlet and the only removal of the affected veins.
The treatment cannot be directed at the etiology of the disease, but the pathogenesis of the problem is known, so it can be stopped. In women, the presence of balls of varicose veins on the legs can be an annoying symptom due to aesthetic problems, but the fair sex is not ready to change the ugly appearance of neglected subcutaneous varicose veins for large wounds. Therefore, the clinics offer cosmetic and radical treatments that have the best patient reviews.
Some anatomy and physiology
The definition of varicose veins is the primary dilation of the subcutaneous venous trunks of the lower extremities, due to congenital, contributing and productive factors. The possibility of being affected by varicose veins exists in 40% of adults on the planet. In developed countries, signs of varicose veins are detected in half of the population.
The saphenous veins in the legs are represented by two large venous systems - the system of the great and small saphenous veins. The great saphenous vein originates in the leg, from where it passes along the inner surface of the leg in the inguinal region, where it flows into the deep vein of the thigh, from the inner part of the common femoral artery.
On the way from the trunk and branches of the great saphenous vein, short venous trunks can be identified - perforators that connect it to the deep veins of the lower leg and thigh, which causes varicose veins away from the main trunks. These perforators are designed to facilitate the passage of blood into the deep venous system.
The small saphenous vein is formed in the external malleolus, is characterized by several turns along the back surface of the lower leg and joins the popliteal vein. Among them, the great and small saphenous veins are connected with special overflows. In the subcutaneous trunks there are numerous venous valves that ensure the movement of blood to the heart and prevent the reverse flow of blood.
Due to the congenital weakness of the venous wall and the load on it, the failure of the internal valve apparatus of the veins develops, the blood begins to move in the opposite direction, causing the saphenous vein to overflow, its further extension and development. of severe varicose veins. Therefore, without eliminating the pathological blood flow, it is impossible to achieve a cure for chronic varicose veins.
The classification of veins with subcutaneous varicose veins in the legs is formed by the name and cause of the development of the disease, the affected venous pool and the stage of chronic venous insufficiency. Varicose veins of the lower extremities are formed by a combination of several factors:
- Congenital distensibility and weakness of the venous wall and increased intravenous pressure.
- Increased pressure on the veins due to a long lifestyle, heavy physical exertion, pregnancy and childbirth.
- Congenital and acquired obstructions to venous outflow (compression syndromes, tumors and bone formations that press on veins.
- Consequences of deep vein thrombosis in the past
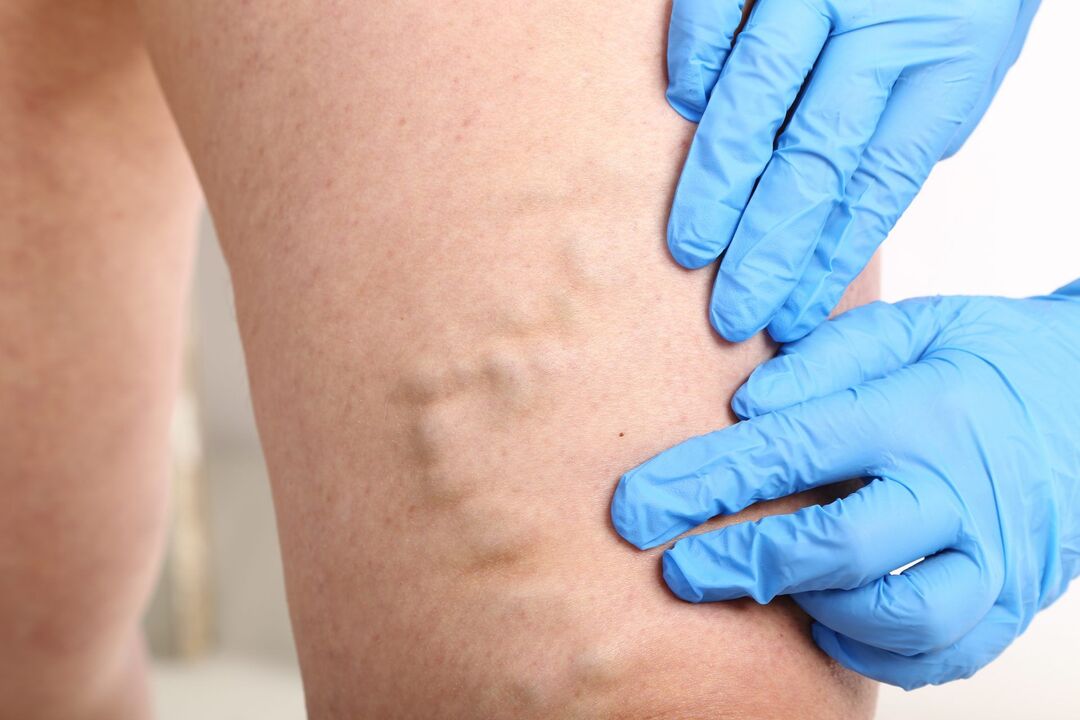
Modern principles of treatment of varicose veins
Many patients often ask the question - what treatment is needed for varicose veins, if only the first signs of it appear. Varicose veins in the legs are a disease that is constantly progressing and prone to complications, therefore, without medical intervention, you cannot count on recovery. Consider the main indications for the treatment of varicose veins in the legs.
Relief of symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency
Venous hypertension is a subjectively unpleasant consequence of impaired venous flow, but varicose veins themselves are not harmful. Symptoms of varicose veins that require prevention and treatment include feelings of heaviness in the legs, swelling in the evening, increased leg fatigue and even pain in the calf muscles. As the disease progresses, stagnation develops in the venous perforators and deep veins, which can lead to hyperpigmentation of the skin, cause eczema in varicose veins, and heaviness in the calves is noted.
The most popular and publicly advertised method of treating the symptoms of varicose veins in the legs is to take various pills for varicose veins, using ointments and creams, which makes contact with specialists delayed. It is important to understand that such tools do not affect the flow of varicose veins, which is why they can slightly relieve complaints and symptoms in the early stages. It is not worth relying on the fact that varicose veins will disappear after treatment with such drugs.
Treatment of complications of varicose veins (trophic ulcers, thrombophlebitis, venous bleeding)
In about 50% of cases, varicose veins are complicated by local inflammatory processes, which expands the indications for active surgical tactics. Most often, the patient comes to treat varicose veins when its complications develop - thrombophlebitis (ICD code I80), which hurts a lot or a trophic ulcer appears. Sometimes disturbed by night cramps in the calf muscles, redness of the skin, pain.
Treatment of thrombophlebitis can be carried out conservatively (heparin ointment, lyoton, compresses) or more actively - removal of affected varicose veins or its coagulation with laser. Clinical recommendations do not give a clear answer to this question, but with an active approach, together with thrombophlebitis, its cause is also removed, and this is varicose veins.
Trophic ulcer is an extreme manifestation of chronic venous insufficiency and is a great danger. It appears as a skin defect in the area of the medial malleolus with active purulent discharge, poor granulation, and is accompanied by persistent damage to the surrounding subcutaneous tissue.
Early varicose ulcers are prone to progression and respond very poorly to conservative treatment. The optimal method of treatment today is the laser correction of the venous exit (EVLK) for varicose veins of the great or small saphenous veins and the correct local treatment (special dressing, washing of the ulcer). One does not work without the other, so it is not necessary to rely on the healing of a trophic ulcer by ointments alone. A mandatory component of treatment is compression therapy with the help of special compression stockings. They greatly alleviate patient complaints.
Cosmetic indications for varicose veins
Varicose veins are a disease that rarely leads to dangerous complications, but often makes you turn to specialists. Swollen varicose veins cause many aesthetic problems for their owners. Usually young patients are embarrassed by these joints and hide their legs. If men are not so afraid of varicose veins and can constantly walk in pants, then women constantly want to walk with their legs open.
The good news is that advanced varicose veins in the legs of women or men can now be eliminated with a single procedure of laser photocoagulation of varicose veins without any trace. Modern interventions are performed without incisions, through minimal punctures, which are absolutely invisible already 3-4 weeks after the intervention. The patient is sent to the operating table under local anesthesia and the operation lasts 40-50 minutes. The laser gives an amazing cosmetic result and a lasting recovery from the manifestations of varicose veins, which is why EVLT is popular with doctors and young patients with varicose veins of the legs at any stage.
Prevention of the development of complications of varicose veins
Solving these problems is possible with conservative and operational methods. The main goal of modern phlebology is to minimize surgical trauma in the treatment of varicose veins with the longest possible therapeutic and cosmetic effect. To solve the first problem it is necessary to block the venous vessels working in the opposite direction, through which a pronounced flow occurs, to solve the second problem it is necessary to remove or turn off the dilated veins from the blood circulation.
Diagnosis of varicose veins
To make an accurate diagnosis of superficial vein disease, an examination by an experienced specialist and ultrasound scanning of the saphenous and deep veins from the abdomen to the legs is necessary. The information from these research methods is sufficient for the correct recognition of this diagnosis in the vast majority of patients. The main signs of varicose veins in the legs can be determined with the naked eye, and the causes can be determined using ultrasound.
In some cases, doctors perform invasive tests on the amount of phlebography in an angiographic unit. After treatment, patients need periodic monitoring of the condition of the operated veins, which doctors perform using ultrasound diagnostics. If at the diagnostic stage the doctor has questions about the state of the deep veins, then MRI or CT diagnostics with contrast accurately determine their patency.
Methods of treatment of varicose veins in the vascular center
A vascular surgeon can cure varicose veins of the lower extremities only by eliminating the causes of its occurrence. It is necessary to fight the cause of the development of varicose veins and the progression of the disease. Consider the main technologies with proven effectiveness.
Varicose Vein Laser Treatment (EVLT)
Endovenous laser coagulation is based on heating the venous wall with a coherent beam of light. Varicose veins can be effectively treated without incisions and general anesthesia. A light-conducting fiber is inserted into a vein through a puncture under ultrasound guidance. Laser energy of a certain wavelength at the moment of its appearance is absorbed by the venous wall, which leads to its heating and the destruction of the connective tissue. As a result, the vein wall turns into scar tissue and blood flow through the affected vein stops completely. The same effect is achieved as with the surgical removal of a vein, but only without incisions, general anesthesia and pain.
In terms of effectiveness, EVLK surpasses open phlebectomy surgery. 98% of all operated patients recover from varicose veins, regardless of the degree of development of the nodes. Rare side effects include numbness of the skin in the area of the clotted vein, inflammation and blood clots in the clotted veins. The overall incidence of such complications does not exceed 1%. At the Innovative Vascular Center, EVLK is the "gold standard", it can cure any varicose veins, both in the initial and advanced stages. Patients leave the best evaluations only after laser treatment.
Radiofrequency ablation of varicose veins (RFO)
In terms of its impact and effect, RFO, like the laser, is referred to as a thermal method for the treatment of varicose veins, but a different physical principle is used there. The radiosonde is also inserted into the vein through a catheter. The intervention is performed with local anesthesia. The RFO principle is based on the generation of thermal energy in the probe head, which is then transferred to the vessel walls. Heating of the wall leads to thermal destruction of its structural elements, followed by scarring of the vein.
Both of these methods (EVLK and RFA) refer to thermoablative (thermal) technologies. In terms of effectiveness, they are similar, however, the laser heats the vein wall itself, while the RFO heats the working surface of the probe, and the heat is transferred to the wall through the liquid part of the blood.
According to experts, EVLT more radically destroys the structure of the affected vein, therefore, after the laser, the frequency of relapses is lower than with radiofrequency ablation. Doctors noted the absence of recurrence of varicose veins in 98% after EVLK and 86% after RFO. Based on 20 years of work experience, phlebologists concluded that thermal methods of varicose veins are treated more effectively than conventional vein removal surgery.
Non-thermal methods of eliminating varicose veins
In the 70s of the XX century, surgeons began to show an increased interest in minimally invasive types of surgical treatment for varicose veins and began to use electrocoagulation. Good idea, but poorly implemented in practice. Patients had skin burns, which may be the reason why doctors were afraid to use thermal methods for a long time with varicose veins. Chemical methods used to remove veins have been proven to be safe and quite effective. These include sclerotherapy in various variants and adhesive removal.
Sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy is the intravenous administration of special drugs that cause damage to the venous wall, followed by the disappearance (overgrowth) of the lumen of the varicose vein. The history of this method began in the 19th century and has an interesting path of development. In the vascular center, specialists use the most advanced technology - a foam form of sclerotherapy. Continuous treatment for six months allows you to get rid of varicose veins of the lower extremities for a long time. Although the recurrence rate is about 50% in 5 years. With sclerotherapy, the treatment does not have a precise focus on the causes of varicose veins, but eliminates the venous nodes themselves, therefore it can be used in combination with other minimally invasive methods (EVLK, RFO). A feature of sclerotherapy is the appearance of dense cones - coagulum at the site of sclerotic veins, which resolve up to six months.
Adhesion of varicose veins with special glue
Venaseal technology is the name of a non-thermal method of eliminating varicose trunks of the saphenous veins, which involves introducing a special adhesive into the lumen of the vein, which polymerizes inside the lumen of the vein, causing its blockage. The idea seems interesting and developed in the last decade, but there are some pitfalls. First, the glue remains inside the affected veins as a foreign body, it does not dissolve. Second, there are risks of periphlebitis around a closed vein, as a reaction of the body to a foreign body. Third, it is an expensive method of treatment.
The cost of treating varicose veins with this method is about twice as expensive as laser photocoagulation. There are no long-term studies regarding the long-term results of such treatment. The advantages of this technology have not yet been identified, but research is being actively conducted, and it is possible that varicose veins will become a disease in which the entire treatment regimen will turn into a "magic" injection. It is characteristic that this method has not yet been considered in the latest clinical guidelines, but is already being actively offered by some phlebological centers.
Surgical methods of treating varicose veins of the lower extremities
Doctors have been dealing with the issue of how to get rid of large superficial varicose veins in the legs and preventing complications since the middle of the 19th century. The history of the struggle with enlarged veins makes it clear how from the early large incisions that disfigure the legs, the operation has moved to micro-punctures, which allow you to deal with varicose veins without cosmetic defects.
Advanced phlebologists use elements of classical surgery in the form of microphlebectomy using punctures to remove varicose veins and individual branches. This may be the most cosmetic method for removing varicose veins in thin skin. A month after such an operation, there is not even a rash on the skin.
Other thermal methods
When deciding how to treat varicose veins, phlebologists often used exotic methods. Varicose veins were treated with thermal exposure using superheated steam and bipolar electrocoagulation. However, modern thermal methods are more effective and they allow the doctor to prevent the further development of varicose veins, and the patient to be treated on an outpatient basis without disrupting his lifestyle. In the hands of a novice phlebologist, thermal removal methods can cause unpleasant complications: decreased sensitivity, burns, seals. The effectiveness of this method in the hands of an experienced phlebologist is more than 98%, and the laser and RFO methods allow you to get rid of not only the initial form, but also the veins with pronounced varicose veins on the legs without incisions.
Using special glue
Since its inception, this method has aroused great interest among phlebologists. It involves gluing the trunk of the great saphenous vein with a special cyanoacrylate glue. In the lumen of the vessel, this adhesive polymerizes and fills the lumen of the dilated vessel. As conceived by the developers, this method does not require any anesthesia and a "plug" appears in the vessel, which reliably blocks the blood flow. Based on this, half an hour is enough for the procedure to eliminate varicose veins in the legs. Venasil is the only technology for the treatment of varicose veins that does not require the wearing of compression stockings.
Most women can return to normal activities immediately. Symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency are relieved immediately after the procedure. The process of active promotion of this glue in the phlebological market should begin in the near future. However, there are some disadvantages: The presence of a foreign body in the human body. Curly glue remains in the container forever and can cause chronic allergies, sometimes there is inflammation of the blood vessel wall or rejection of the polymer by suffocation. Acute thrombophlebitis of the adjacent vessel may occur.
The use of glue on the trunk of the great saphenous vein does not eliminate the need to deal with the elimination of varicose branches, so doctors will have to remove the signs of subcutaneous varicose veins with sclerotherapy or miniphlebectomy. The visible effect of using the adhesive is manifested only in the case of combination with other methods of eliminating varicose veins. The patient has to pay more. The unreasonably high cost of the gluing kit makes this procedure much more expensive than the modern laser or radiofrequency method.
In the clinic, preference is given to thermal methods. Phlebologists believe that it is better to use good local anesthesia than to treat varicose veins in the legs with an expensive and untested method. Moreover, the result is the same at best. In the event that a relapse occurs, the patient will have to undergo a complex operation to remove the closed vessel, as other methods will no longer be applicable.
The modern method of combined treatment of reflux along subcutaneous venous trunks adds weight to conventional sclerotherapy. Mechanical-chemical procedures are understood as a combination of mechanical damage to the inner surface of the venous wall and the introduction of a sclerosing agent. A catheter is inserted into the main saphenous vein through a puncture under ultrasound guidance. After installing the catheter in the right place, the device is connected. The sharp rotating head of the catheter makes up to 3. 5 thousand rotations per minute, causing significant damage to the inner layer of the venous wall. In parallel, a sclerosing agent is injected through the catheter, which "mixes" into the lumen of the vessel and with the help of the rotating part of the catheter, acts on the vascular wall, causing its inflammation and adhesion.
This is a modern aesthetic microsurgical method for the removal of varicose veins. It implies a delicate technique of drilling and pulling varicose branches with the help of special tools. This operation is not for a novice phlebologist, you need to master the skills of delicate operation. Miniphlebectomy is an operation without the use of a scalpel and is performed under local anesthesia. Punctures are performed in the direction of the skin lines, so after 2 months they are almost invisible.